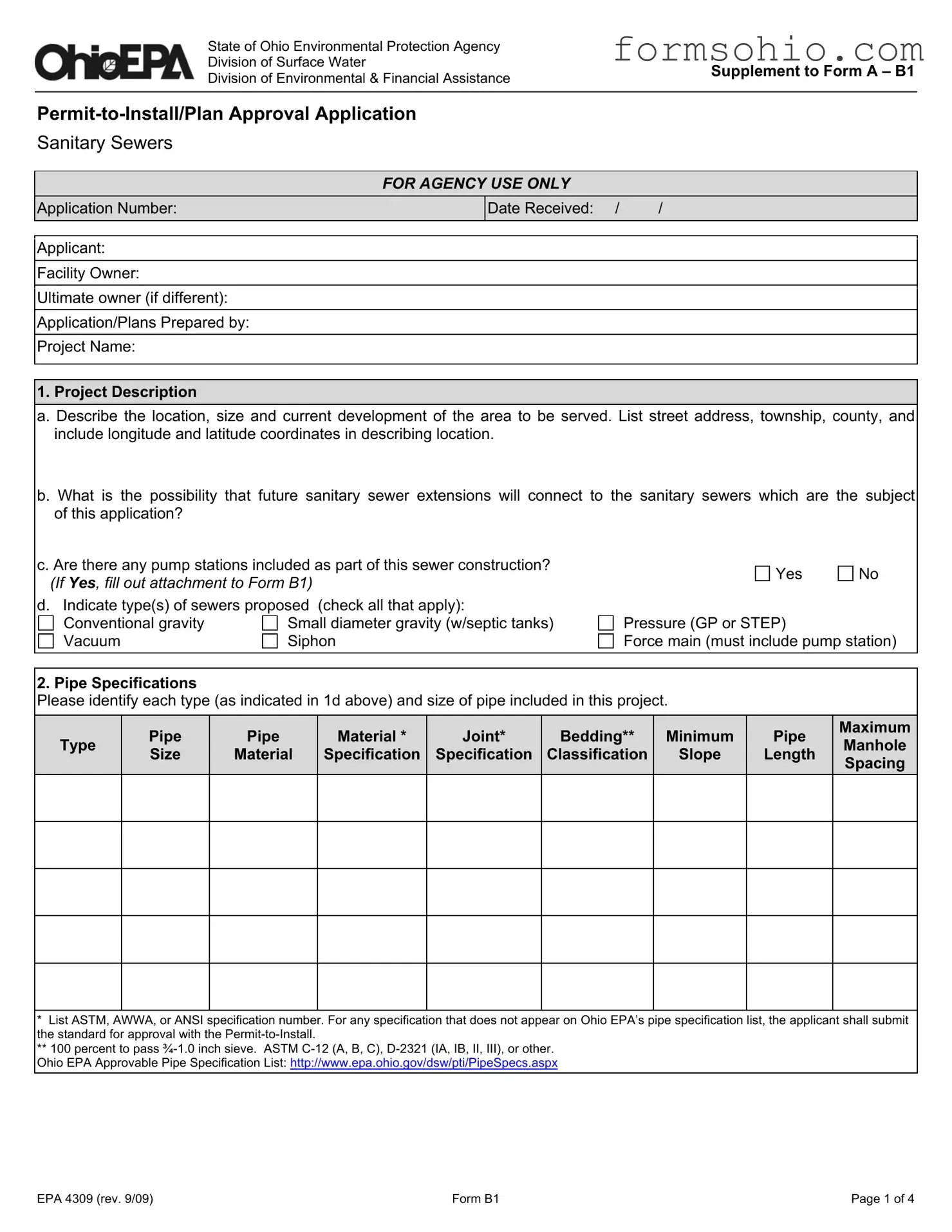
Filling out the Ohio EPA 4309 form can be a complex task. Many applicants make mistakes that can delay the approval process. One common mistake is failing to provide complete project descriptions. This includes not detailing the location, size, and current development of the area. It is essential to include specific information such as the street address, township, county, and even longitude and latitude coordinates.
Another frequent error is neglecting to indicate whether there are any pump stations included in the sewer construction. If pump stations are part of the project, the applicant must fill out the necessary attachment to Form B1. Omitting this information can lead to complications later in the review process.
Applicants often miscalculate the expected design flows for the proposed sewer. This includes both start-up and peak hourly flows. It is crucial to provide accurate figures based on the current and planned area served. Inaccurate calculations can raise concerns about the hydraulic capacity of the sewer, leading to potential rejections.
Many people overlook the importance of confirming whether the receiving wastewater treatment facility has adequate capacity. If the facility cannot handle the anticipated flows, the applicant must explain the steps being taken to address this issue. Failure to provide this information can result in delays or denials.
Another common mistake involves the design of the sewers themselves. Applicants sometimes do not ensure that the sewers are deep enough to serve adjacent basements or prevent freezing. These design flaws can lead to significant problems down the line, including potential structural issues.
Inadequate attention to stream protection is also a mistake that applicants make. If there are stream crossings, it is vital to fill out the stream evaluation addendum accurately. Not addressing these concerns can lead to environmental damage and further complications with the application.
Manhole design is another area where errors can occur. Applicants must specify the type of manhole, material specifications, and whether watertight frames and covers are used. Missing this information can result in compliance issues during construction.
Additionally, the protection of water supplies is often overlooked. If there are physical connections between the sewer and a potable water supply system, this must be clearly indicated. Not addressing these connections can lead to contamination risks and regulatory penalties.
Lastly, ensuring that all necessary submittals are included with the application is crucial. Missing documents can lead to delays in processing. Applicants should double-check that they have included all required copies of plans, technical specifications, and any additional forms needed.




 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No
 No
No